end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. More Than Just a Number.

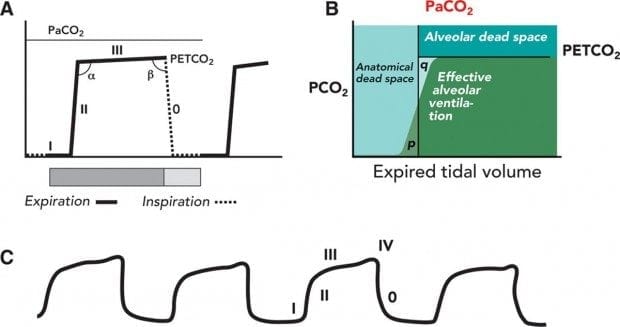
A Time Capnogram Of A Patient With Airflow Obstruction Illustrating A Download Scientific Diagram
Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for.
. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in patients meeting the criteria. End tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest. End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiac Arrest.
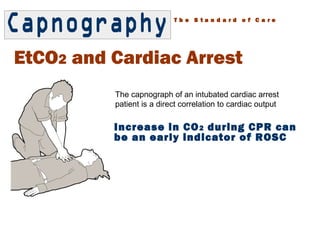
Renowned Cardiac Specialists Offer Treatments Diagnosis for Heart Vascular Diseases. Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to build up in the bloodstream the initial ETCO2 reading may initially be higher than the normal 35-45 mm Hg range as it gets washed out of. Increasing CO2 during CPR can also indicate the return of spontaneous circulation.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. A prospective observational study. End-Tidal CO2 as a Predictor of Cardiac Arrest Survival.
Geoff Murphy from Master Your Medics provides a refresher training video on end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest. Ad View a brochure to learn about end-tidal CO2 capnography. Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC.
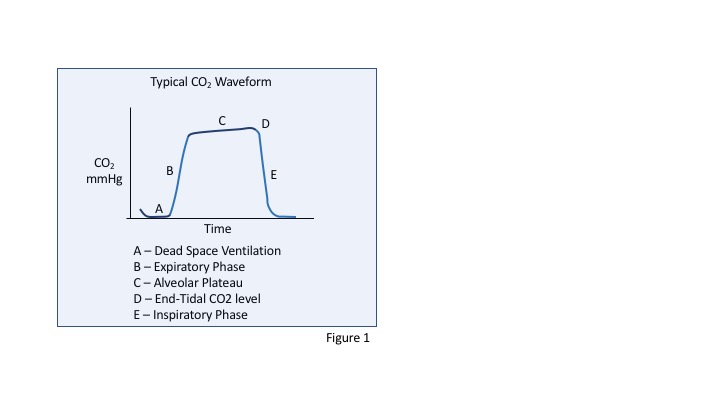
Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
Predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC. Ad Awarded Best Hospitals Ranking by US News For Cardiology Heart Surgery. After 20 minutes of advanced cardiac life support ETCO2 averaged 39 - 28 mm Hg range 0 to 12 mm Hg in patients in whom the theoretical decision was made to cease field resuscitation.
These values are approximately 14 the normal EtCO2 35-45 mm Hg and ideal CPR will provide at least 14 of cardiac output. ROSC is reflected by a sudden rise in EtCO2. End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients.
Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S. BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO 2 ET-CO 2 provides instantaneous information about ventilation how effectively CO. Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14.
End-Tidal CO2 as a Predictor of Cardiac Arrest Survival. During precordial compression it increased to 10 - 05 percent. CO2 will decrease prior to a cardiac arrest in patients that are intubated in an intensive care setting.
In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was associated with an almost five-fold higher rate of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. This is an example of capnography during CPR. Multiple monitoring options so you can choose what and how to monitor respiratory status.
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. Because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not. In addition a decrease in the EtCO2 during resuscitative events of 25 was associated with a.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. The Journal of Emergency Medicine released an article traumatic brain injury careOriginal Article.
In contrast Varon et al. Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS.
Carbon Dioxide Detector Article

Sudden Decrease In End Tidal Carbon Dioxide In A Neonate Undergoing Surgery For Type B Interrupted Aortic Arch

Pediatric Advanced Life Support Ppt Download

Brief Summary Of The Experimental Protocol Ca Cardiac Arrest Cpr Download Scientific Diagram

353emf Elevation Of The Head And Thorax During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Improves Cerebral Blood Flow In A Swine Model Of Prolonged Cardiac Arrest Annals Of Emergency Medicine
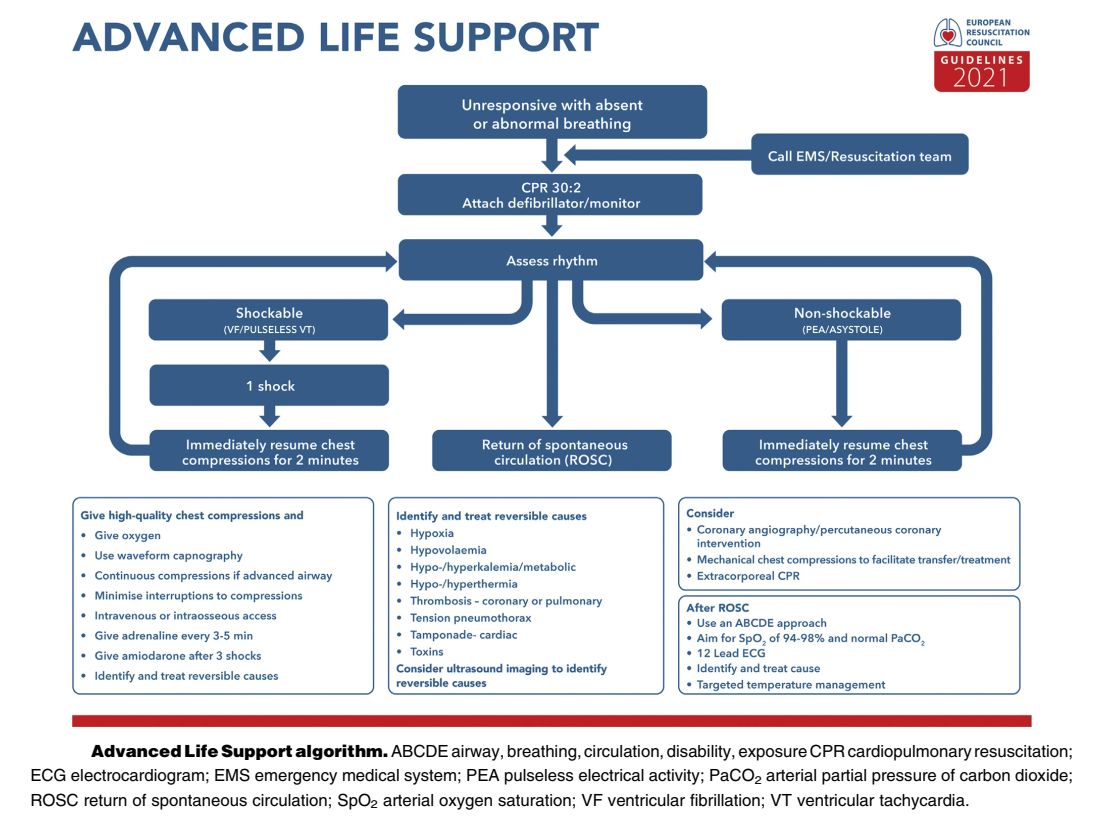
The Erc Guidelines 2021 Adult Advanced Life Support Part 3 7

A Time Capnogram Of A Patient With Airflow Obstruction Illustrating A Download Scientific Diagram

Etco2 1a Peco2 1b Vco2 1c For Survivors Vs Download Scientific Diagram
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
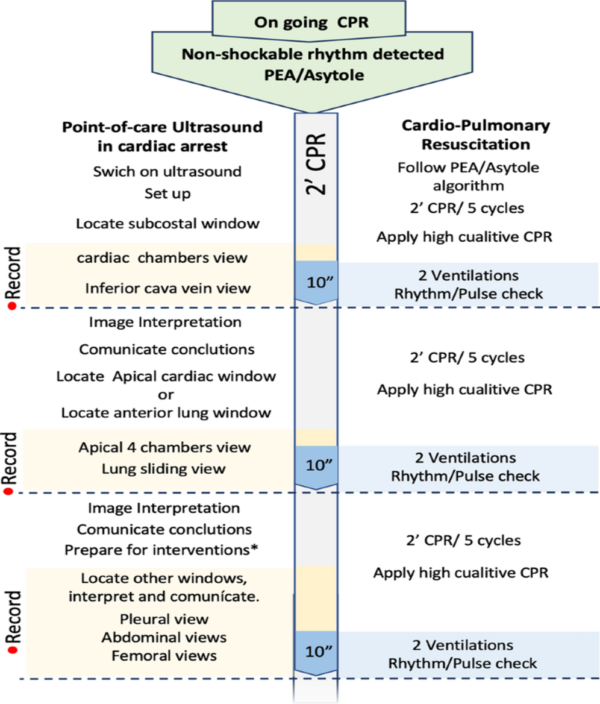
Podcast Cardiac Arrest Pocus Integration Communication Strategies E Cpr Calling The Code האיגוד הישראלי לרפואה דחופה